1.00489
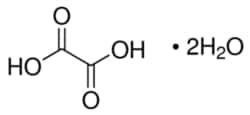
Oxalic acid dihydrate
Suprapur®
Manufacturer: Supelco
CAS Number: 6153-56-6
Synonym(S): Oxalic acid dihydrate, Ethanedioic acid
Select a Size
| Pack Size | SKU | Availability | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 G | 1.00489-100-G | In Stock | ₹ 34,199.99 |
1.00489 - 100 G
In Stock
Quantity
1
Base Price: ₹ 34,199.99
GST (18%): ₹ 6,155.998
Total Price: ₹ 40,355.988
grade
for inorganic trace analysis
Quality Level
100
vapor pressure
0.000312 hPa ( 25 °C)
Assay
≥99.5% (calculated as dihydrate, alkalimetric)
form
solid
potency
375 mg/kg LD50, oral (Rat)
pH
1.5 (10 g/L in H2O)
bp
149-160 °C/1013 hPa (decomposition)
mp
98-100 °C
transition temp
flash point 157 °C (decomposition)
Other Options
Related Products
Description
- Application: Reaction Atmosphere-Controlled Thermal Conversion of Ferrocene to Hematite and Cementite Nanomaterials-Structural and Spectroscopic Investigations.: This study investigates the conversion of ferrocene to hematite and cementite nanomaterials under controlled thermal conditions. The structural and spectroscopic properties of the resulting materials were analyzed, providing insights into their potential applications in various fields of chemistry and materials science (Kundu et al., 2024). Insights into a Co-precursor Driven Solid-State Thermal Reaction of Ferrocene Carboxaldehyde Leading to Hematite Nanomaterial: A Reaction Kinetic Study.: This research focuses on the solid-state thermal reaction of ferrocene carboxaldehyde with oxalic acid dihydrate, leading to hematite nanomaterial. The study provides detailed reaction kinetics and potential applications in catalysis and materials science (Chakraborty et al., 2023). Supramolecular Structure of Microwave Treated Bamboo for Production of Lignin-Containing Nanocellulose by Oxalic Acid Dihydrate.: The paper explores the use of oxalic acid dihydrate in the microwave treatment of bamboo to produce lignin-containing nanocellulose. This process enhances the material properties of nanocellulose, offering applications in sustainable materials and bioengineering (Wang et al., 2023). Thermo-Mechano-Chemical Deconstruction of Cellulose for Cellulose Nanocrystal Production by Reactive Processing.: This study presents a method for producing cellulose nanocrystals using thermo-mechano-chemical deconstruction with oxalic acid dihydrate. The resulting nanocrystals have potential uses in biocomposites and nanomaterials (Guiao et al., 2022). Formation and Structure Evolution of Starch Nanoplatelets by Deep Eutectic Solvent of Choline Chloride/Oxalic Acid Dihydrate Treatment.: This research investigates the formation of starch nanoplatelets using a deep eutectic solvent comprising choline chloride and oxalic acid dihydrate. The study highlights the structural evolution and potential applications in food science and materials engineering (Xiao et al., 2022).
- Analysis Note: Assay (alcalimetric, calc. as dihydrate): ≥ 99.5 %Chloride (Cl): ≤ 5000 ppbPhosphate (PO₄): ≤ 500 ppbSulfate (SO₄): ≤ 2000 ppbAg (Silver): ≤ 10 ppbAl (Aluminium): ≤ 20 ppbAs (Arsenic): ≤ 1.0 ppbAu (Gold): ≤ 1.0 ppbBa (Barium): ≤ 100 ppbBe (Beryllium): ≤ 1.0 ppbBi (Bismuth): ≤ 1.0 ppbCa (Calcium): ≤ 100 ppbCd (Cadmium): ≤ 50 ppbCo (Cobalt): ≤ 5 ppbCr (Chromium): ≤ 10 ppbCu (Copper): ≤ 5 ppbFe (Iron): ≤ 50 ppbGa (Gallium): ≤ 1.0 ppbGe (Germanium): ≤ 1.0 ppbIn (Indium): ≤ 1.0 ppbK (Potassium): ≤ 200 ppbLi (Lithium): ≤ 5 ppbMg (Magnesium): ≤ 20 ppbMn (Manganese): ≤ 5 ppbMo (Molybdenum): ≤ 5 ppbNa (Sodium): ≤ 100 ppbNi (Nickel): ≤ 10 ppbPb (Lead): ≤ 10 ppbPt (Platinum): ≤ 1.0 ppbSb (Antimony): ≤ 1.0 ppbSn (Tin): ≤ 5 ppbSr (Strontium): ≤ 100 ppbTi (Titanium): ≤ 5 ppbTl (Thallium): ≤ 1.0 ppbU (Uranium): ≤ 1.0 ppbV (Vanadium): ≤ 10 ppbZn (Zinc): ≤ 20 ppb
- Legal Information: SUPRAPUR is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
SAFETY INFORMATION
Pictograms
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
P264 - P280 - P301 + P312 - P302 + P352 + P312 - P305 + P351 + P338 - P362 + P364
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Dermal - Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Eye Dam. 1
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Compare Similar Items
Show Difference
grade: for inorganic trace analysis
Quality Level: 100
vapor pressure: 0.000312 hPa ( 25 °C)
Assay: ≥99.5% (calculated as dihydrate, alkalimetric)
form: solid
potency: 375 mg/kg LD50, oral (Rat)
pH: 1.5 (10 g/L in H2O)
bp: 149-160 °C/1013 hPa (decomposition)
mp: 98-100 °C
transition temp: flash point 157 °C (decomposition)
grade:
for inorganic trace analysis
Quality Level:
100
vapor pressure:
0.000312 hPa ( 25 °C)
Assay:
≥99.5% (calculated as dihydrate, alkalimetric)
form:
solid
potency:
375 mg/kg LD50, oral (Rat)
pH:
1.5 (10 g/L in H2O)
bp:
149-160 °C/1013 hPa (decomposition)
mp:
98-100 °C
transition temp:
flash point 157 °C (decomposition)