Cytochrome c Antibody (CTC05), Novus Biologicals™
Mouse Monoclonal Antibody
Manufacturer: Fischer Scientific
The price for this product is unavailable. Please request a quote
Antigen
Cytochrome c
Concentration
0.2mg/mL
Applications
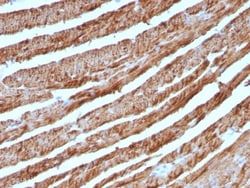
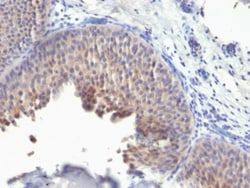
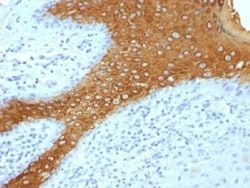
Western Blot, Flow Cytometry, Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin), Immunofluorescence
Conjugate
Unconjugated
Host Species
Mouse
Research Discipline
Apoptosis, Cellular Markers, Cholesterol Metabolism, Core ESC Like Genes, Lipid and Metabolism, Mitochondrial Markers, Stem Cell Markers
Formulation
1.0mM PBS and 0.05% BSA with 0.05% Sodium Azide
Gene ID (Entrez)
54205
Immunogen
Recombinant cytochrome c protein
Primary or Secondary
Primary
Content And Storage
Store at 4C.
Molecular Weight of Antigen
15 kDa
Clone
CTC05
Dilution
Western Blot 0.5 - 1.0 ug/ml, Flow Cytometry 0.5 - 1 ug/million cells in 0.1 ml, Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin 0.25 - 0.5 ug/ml, Immunofluorescence 0.5 - 1.0 ug/ml
Classification
Monoclonal
Form
Purified
Regulatory Status
RUO
Target Species
Human, Mouse, Rat, Amphibian, Avian, Canine, Drosophila, Equine
Gene Alias
CYCHCS, cytochrome c, cytochrome c, somatic, THC4
Gene Symbols
CYCS
Isotype
IgG2b κ
Purification Method
Protein A or G purified
Test Specificity
Cytochrome C is a well-characterized mobile electron transport protein that is essential to energy conversion in all aerobic organisms. In mammalian cells, this highly conserved protein is normally localized to the mitochondrial inter-membrane space. More recent studies have identified cytosolic cytochrome c as a factor necessary for activation of apoptosis. During apoptosis, cytochrome c is trans-located from the mitochondrial membrane to the cytosol, where it is required for activation of caspase-3 (CPP32). Overexpression of Bcl-2 has been shown to prevent the translocation of cytochrome c, thereby blocking the apoptotic process. Overexpression of Bax has been shown to induce the release of cytochrome c and to induce cell death. The release of cytochrome c from the mitochondria is thought to trigger an apoptotic cascade, whereby Apaf-1 binds to Apaf-3 (caspase-9) in a cytochrome c-dependent manner, leading to caspase-9 cleavage of caspase-3.
Description
- Ensure accurate, reproducible results in Western Blot, Flow Cytometry, Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin), Immunofluorescence Cytochrome c Monoclonal specifically detects Cytochrome c in Human, Mouse, Rat, Amphibian, Avian, Canine, Drosophila, Equine, Pigeon samples
- It is validated for Western Blot, Flow Cytometry, Immunohistochemistry, Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence, Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin.